CoreML Usage
About CoreML
- Support image processing for Vision.
- Support NPL (natural language processing) for Foundation.
- Support learned decision tree analyzing for GameplayKit.
CoreML and Vision
- CoreML makes it even easier to use trained models in your apps.
- Vision gives you easy access to Apple’s models for detecting faces, face landmarks, text, rectangles, barcodes, and objects.
Because these two frameworks are built on Metal, they run efficiently on the device, so you don’t need to send your users’ data to a server.
Model Usage
When you load a trained machine learning model (.mlmodel) into xcode, the screenshot is like (take inceptionv3.mlmodel as an example):
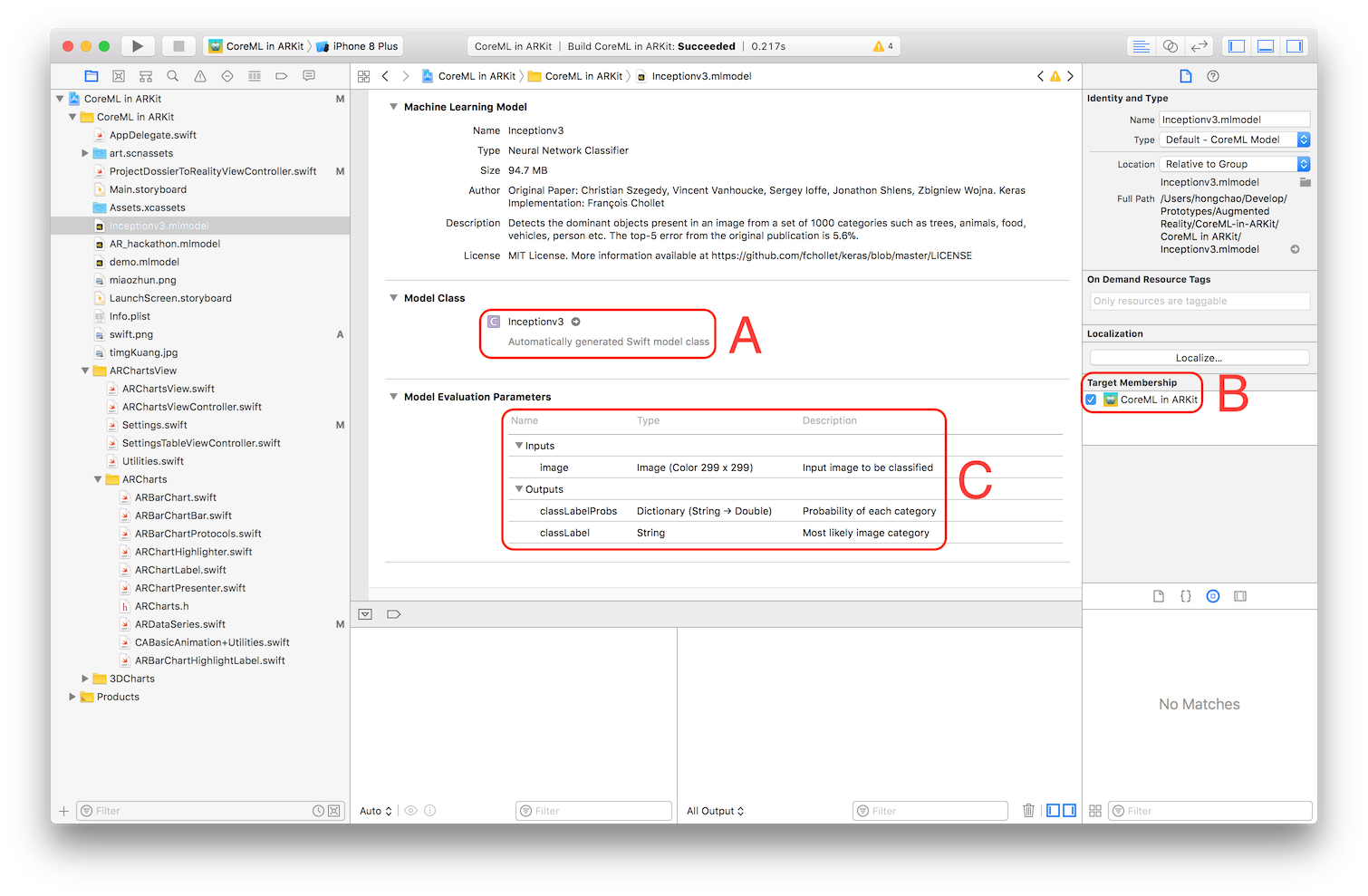
From Model Class (section A), we can see that xcode has Automatically generated Swift model calss. Click the right arrow to view the generated model class.
If the model class is not generated successfully, double check Target Membership (section B) to make sure the mlmodel file is added into the correct target.
From Model Evaluation Parameters(section C), we can see the input and output of the trained model.
The following is a sample usage of image classification model:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 | |
Refer to Build more intelligent apps with machine learning for some official materials.
For some detailed usage step by step, refer to Core ML and Vision: Machine Learning in iOS 11 Tutorial.
Model Training
Basic

Microsoft Custom Vision supplies a very friendly UI interface. You can upload you images and label them very easily. After training is done, you can export the model for mobile devices, including: mlmodel file for iOS platform, and TensorFlow model on Android platform.
Friendly UI Interface:
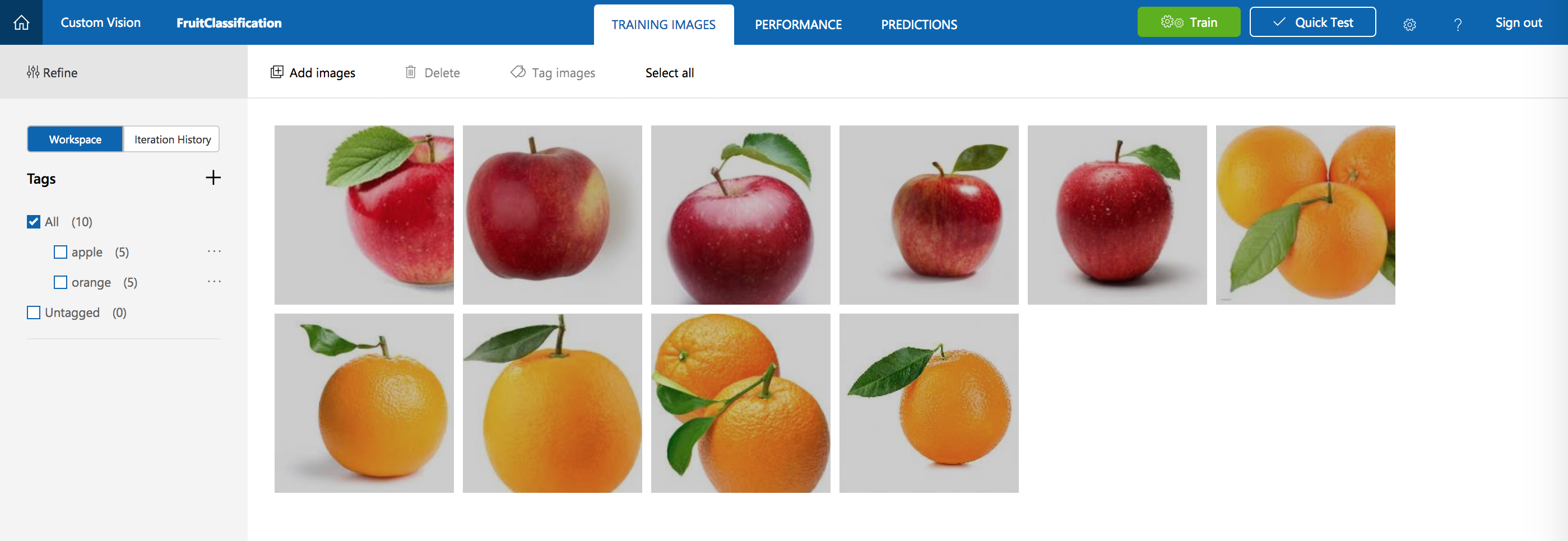
But there are some limitations, as Custom Vision is still in preview process.
Advanced
apple turicreate image classification supplies more configurations for model training, like the partition of trainning data and verification data. But some Python experience is needed.
CoreML Pros and Cons
Pros
Easy to use. As described at the beginning of the post.
High performance. As is said:
“It was amazing to see the prediction results immediately without any time interval.”
Cons
Lack of federated learning. As is said:
There are no provisions within Core ML for model retraining or federated learning, where data collected from the field is used to improve the accuracy of the model. That’s something you would have to implement by hand, most likely by asking app users to opt in for data collection and using that data to retrain the model for a future edition of the app.
Refer to Apple’s Core ML: The pros and cons.