事件循环中的Macrotask和Microtask
For details, refer to Event loop: microtasks and macrotasks.
Event Loop
The event loop concept is very simple. There’s an endless loop, where the JavaScript engine waits for tasks, executes them and then sleeps, waiting for more tasks.
For instance, while the engine is busy executing a script, a user may move their mouse causing mousemove, and setTimeout may be due and so on, these tasks form a queue.
Tasks from the queue are processed on “first come – first served” basis. When the engine browser is done with the script, it handles mousemove event, then setTimeout handler, and so on.
So far, quite simple, right?
Two more details:
- Rendering never happens while the engine executes a task. It doesn’t matter if the task takes a long time. Changes to the DOM are painted only after the task is complete.
- If a task takes too long, the browser can’t do other tasks, such as processing user events. So after a time, it raises an alert like “Page Unresponsive”, suggesting killing the task with the whole page. That happens when there are a lot of complex calculations or a programming error leading to an infinite loop.
Event Loop应用 Use-case 1: splitting CPU-hungry tasks Use case 2: progress indication Use case 3: doing something after the event
Macrotasks and Microtasks
- Macrotask:
script,mousemove,setTimeout- use
setTimeout(f)to dispatch a callback as a macrotask
- Microtask:
- They are usually created by promises: an execution of
.then/catch/finallyhandler becomes a microtask. - use
queueMicrotask(f)to dispatch a callback as a microtask
- They are usually created by promises: an execution of
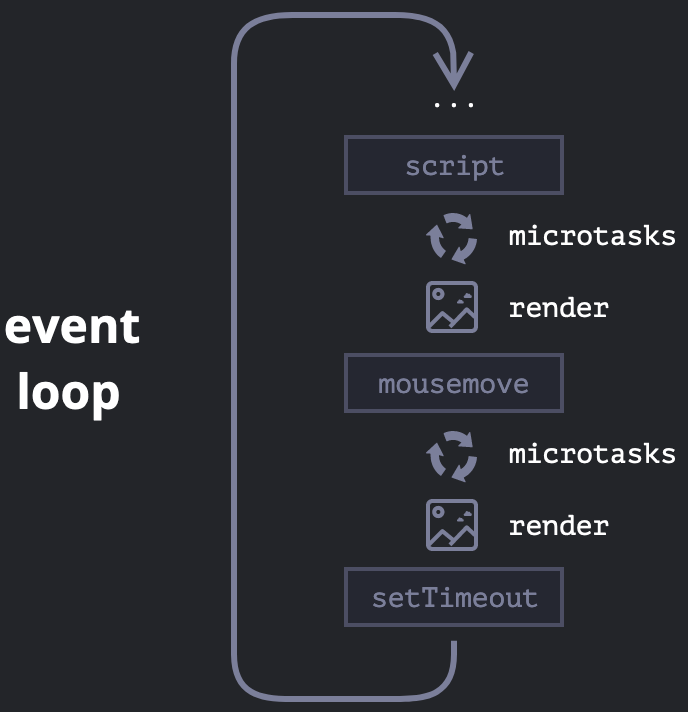
Event loop workflow with macrotask and microtask:
Summary
A more detailed event loop algorithm (though still simplified compared to the specification):
1. Dequeue and run the oldest task from the macrotask queue (e.g. “script”).
2. Execute all microtasks:
* While the microtask queue is not empty:
* Dequeue and run the oldest microtask.
3. Render changes if any.
4. If the macrotask queue is empty, wait till a macrotask appears.
5. Go to step 1.
If you want a real parallel task execution, use Web Worker. it is running in a separate thread.
练习
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | |
答案:The console output is:
1
| |